Element Carbon Cycle Lab
The CarbonCycleLab (CCLab) at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a research platform that focuses on the development of technologies for the circular economy and green hydrogen. CCLab investigates processes for converting residual materials and waste into high-quality chemical base materials that can be used as substitutes for fossil raw materials in industry. The central process involves the pyrolysis of waste, followed by the conversion of intermediate products into synthesis gases such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide. These are used to produce important chemicals such as methanol. CCLab thus supports the goals of the European Green Deal and contributes to the creation of a sustainable, climate-neutral economy.
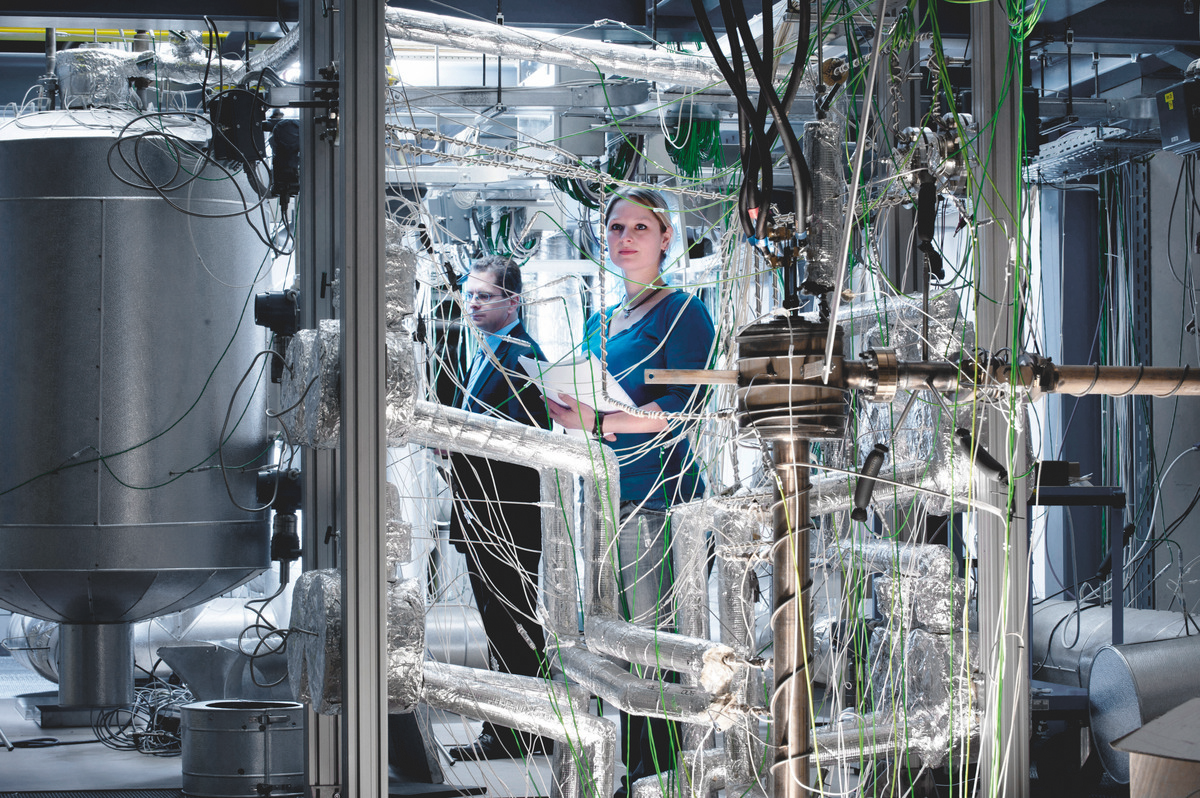
FLUTE
FLUTE (Far Infrared Linac and Test Experiment) at the Institute for Beam Physics and Technology (IBPT) at KIT is an accelerator test facility for a wide range of accelerator physics studies. FLUTE generates ultra-short electron bunches in the femtosecond to picosecond range and produces intense terahertz radiation. The parameters of the accelerator, such as electron bunch length, charge, repetition rate, and energy, can be varied over a wide range, enabling a variety of experiments in physics, with new technologies, but also novel applications in materials science and medicine.
The FLUTE research infrastructure is available to all students in the form of summer courses, theses and excursions.
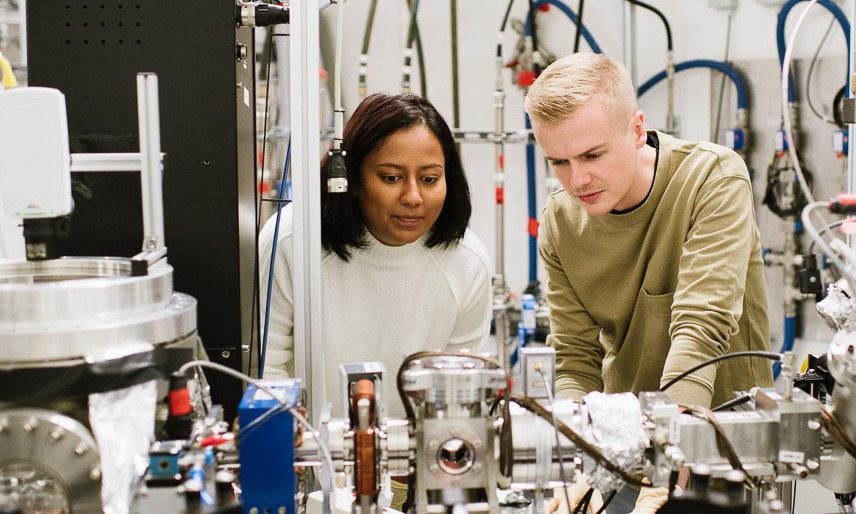
KALLA
The Karlsruhe Liquid Metal Laboratory (KALLA) is a specialized research center at the Institute for Thermal Energy Technology and Safety (ITES) of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). KALLA is dedicated to the intensive study of liquid metals, which play a key role in modern energy generation and storage technologies. The research focuses in particular on high-temperature applications in which liquid metals are of outstanding importance due to their thermal and physical properties. Research activities include the analysis of thermofluid dynamics, magnetohydrodynamics and the development of innovative high-temperature heat storage systems. The aim is to tap into and further develop liquid metals as high-performance materials for future applications in nuclear technology, renewable energy generation and other demanding energy systems.
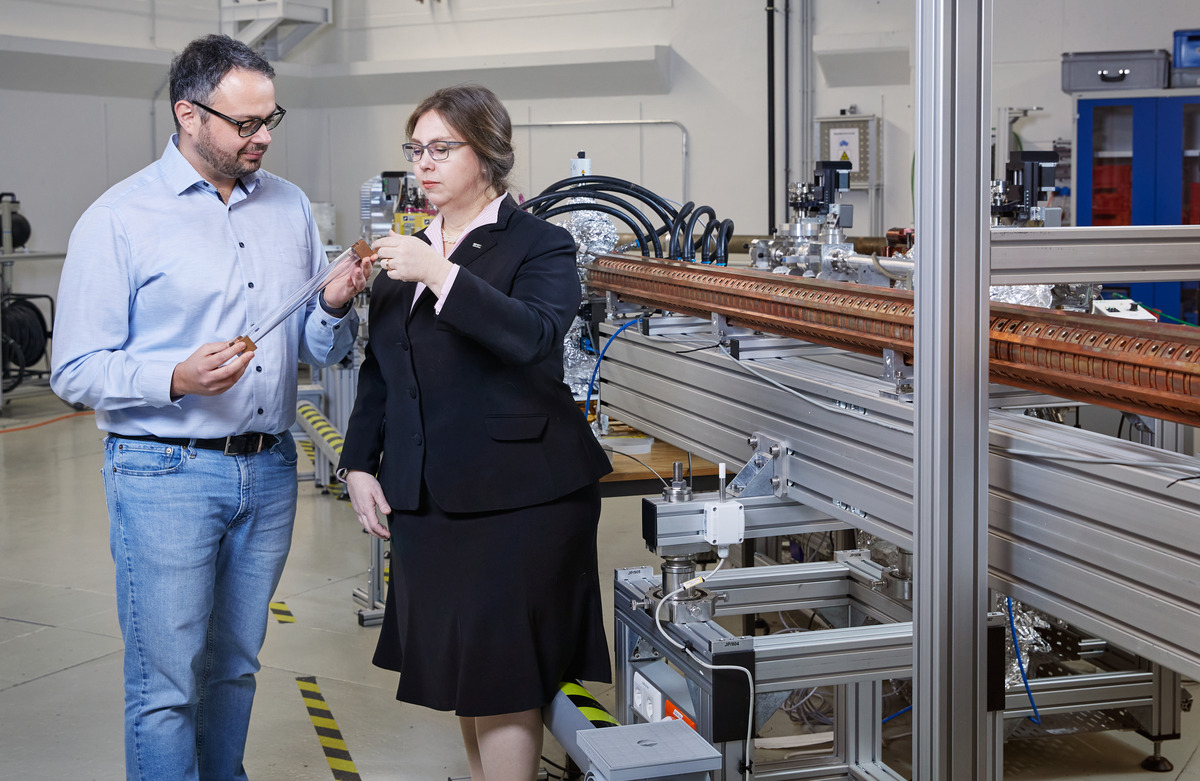
KARA
KARA (Karlsruhe Research Accelerator) at the Institute for Beam Physics and Technology (IBPT) at KIT is an accelerator test facility that generates relativistic electrons and synchrotron radiation. KARA enables research into new accelerator technologies and the investigation of renewable energies for the operation of large infrastructures in the KIT test field KITTEN in collaboration with the Energy Lab at KIT. KARA offers a variety of testing opportunities for the development of new technologies, particularly in the fields of accelerators, lasers, electro-optics, artificial intelligence (AI), high-temperature superconducting magnets, medicine, materials science, and much more. KARA is used for both scientific and industrial applications and enables high-precision measurements and analyses.
The KARA research infrastructure is available to all students in the form of summer courses, theses and excursions.
KITTEN
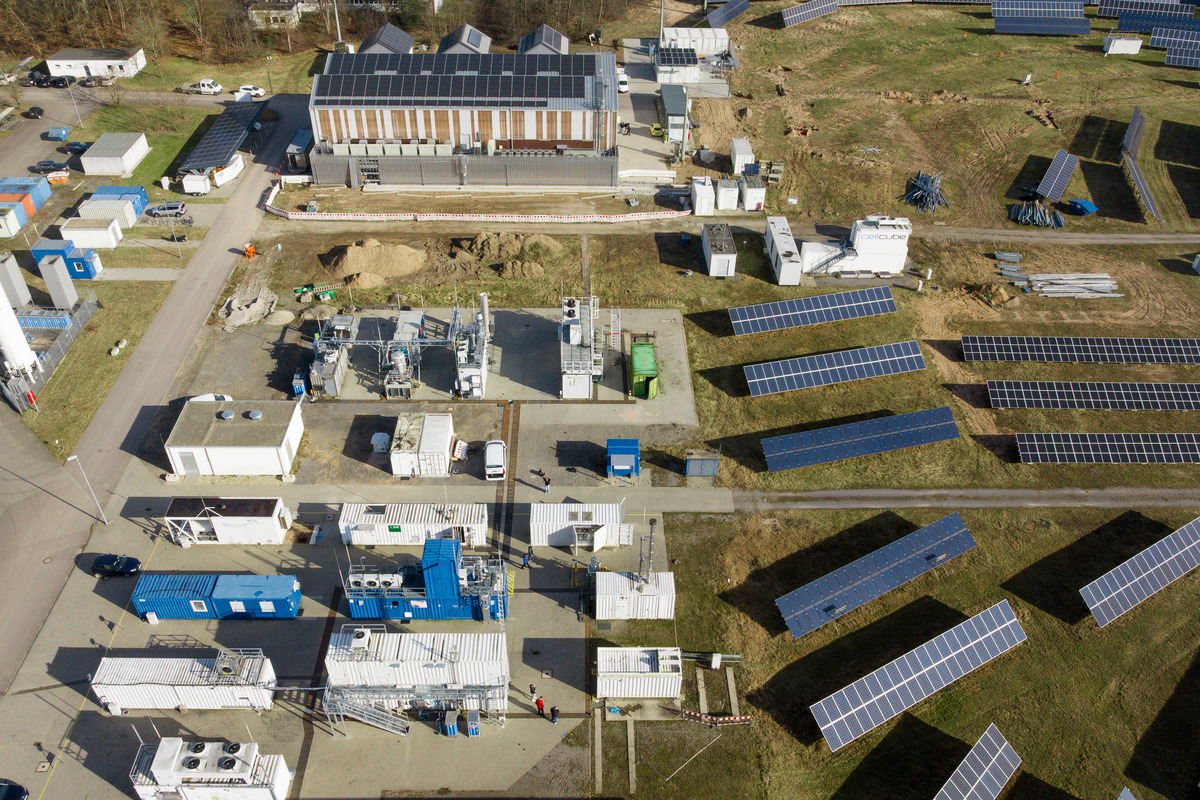
The KIT Test Field for Energy Efficiency and Grid Stability in Large Research Infrastructures (KITTEN) combines Europe's largest research laboratory for renewable energy, the Energy Lab, with the Karlsruhe Research Accelerator (KARA) test facility for accelerator technologies. The aim is to operate large-scale research facilities such as particle accelerators efficiently and sustainably. The theoretical concepts developed are experimentally validated directly under real conditions with regard to physical and technical aspects - a unique combination worldwide. In this way, the KITTEN project is paving the way for energy-responsible and therefore sustainable research on a large scale.
KITTEN is available to all students in the form of summer courses, theses and excursions.
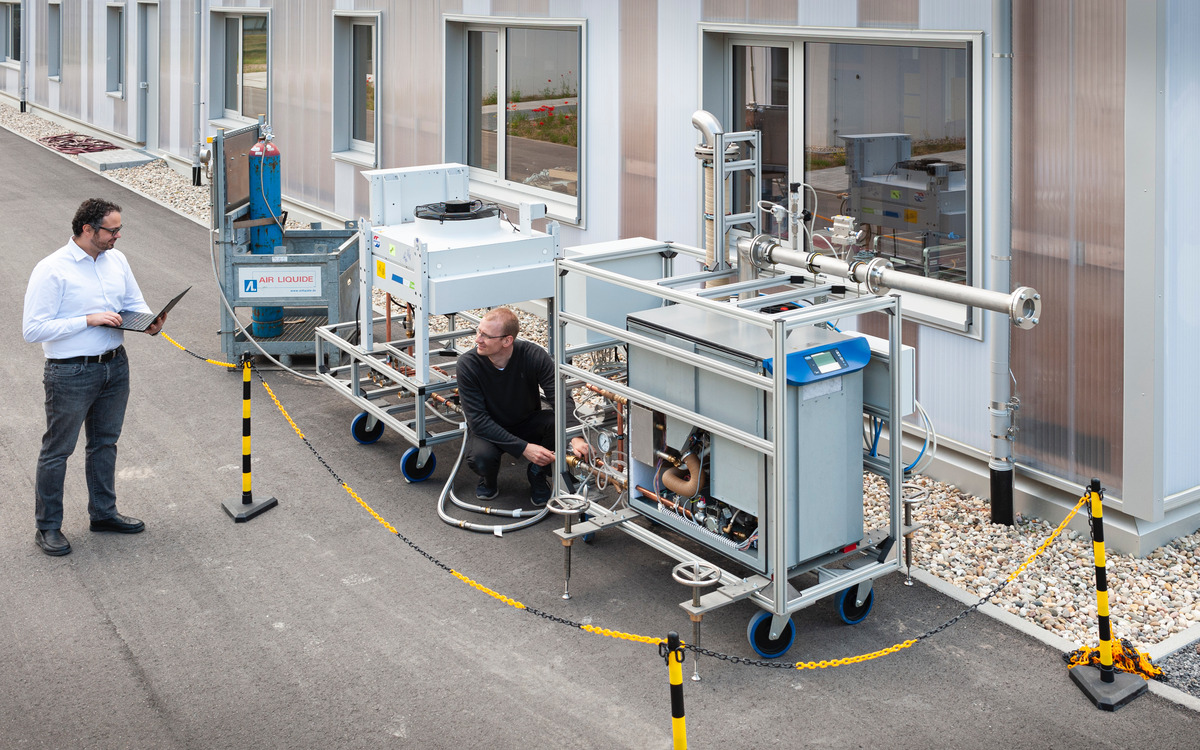
Power-to-X Lab (P2XLab)
The P2XLab at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is an innovative research center that focuses on the conversion of surplus green electricity into chemical energy carriers. In specially developed facilities, processes such as power-to-liquid (e-fuels) and power-to-gas (climate-neutral methane) are investigated in order to optimize the storage and use of renewable energy. The P2XLab is a central component of the Energy Lab and makes an important contribution to the energy transition by developing sustainable storage and conversion technologies.
Students can contribute to P2XLab in the form of final theses and compulsory work.